Precision Matters: A Guide to Injection Mold Manufacturing for Electronics
Understanding Injection Mold Manufacturing
The world of electronics is ever-evolving, demanding precision and efficiency in every component. One critical process that ensures the reliability and quality of electronic components is injection mold manufacturing. This method is essential for producing high-quality plastic parts used in various electronic devices, from smartphones to complex medical equipment.
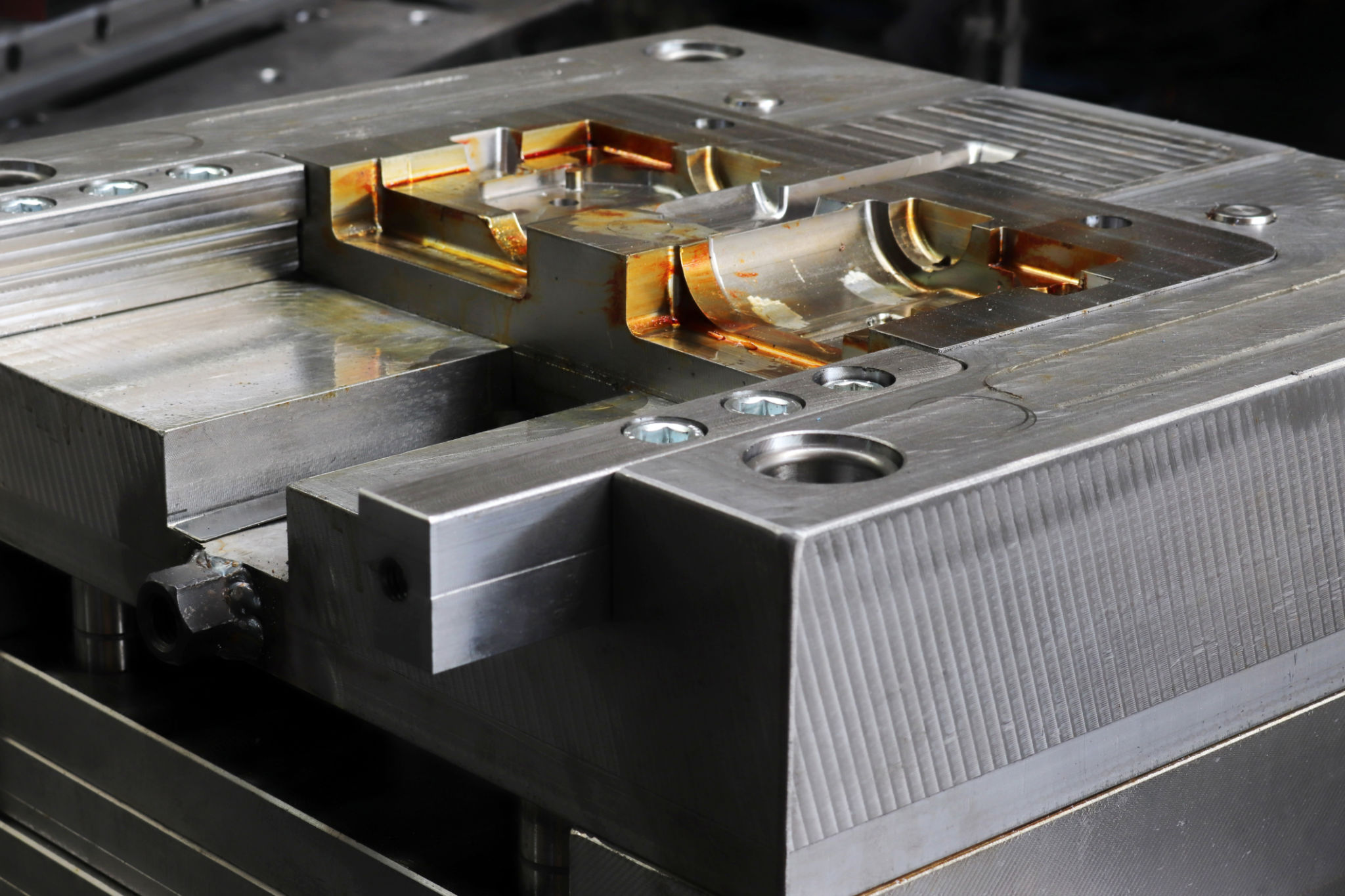
Injection molding involves injecting molten material into a mold cavity, where it cools and solidifies to form the desired part. This method is renowned for its ability to produce complex shapes with impeccable precision. For electronics, this precision ensures that each component fits perfectly, reducing the risk of malfunction.
The Importance of Precision in Electronics
With electronics, even the smallest deviation can lead to significant problems. Components must fit together seamlessly to ensure functionality and longevity. Precision in injection mold manufacturing is crucial for maintaining the tight tolerances required in electronic components.
Moreover, as electronic devices become more compact, the need for smaller, more precise parts increases. Injection molding allows manufacturers to achieve these tiny dimensions without sacrificing quality or performance.
Key Steps in Injection Mold Manufacturing
The injection mold manufacturing process consists of several critical steps:
- Designing the Mold: The first step involves creating a detailed design of the mold, ensuring it meets the specifications required for the electronic component.
- Mold Fabrication: Once the design is finalized, the mold is fabricated using high-precision machines.
- Injection Molding: The molten material is injected into the mold cavity at high pressure.
- Cooling and Ejection: After cooling, the newly formed part is ejected from the mold.

Materials Used in Injection Molding
The choice of material is crucial in injection mold manufacturing for electronics. Common materials include thermoplastics like ABS, polycarbonate, and polypropylene. These materials are chosen for their durability, heat resistance, and ability to withstand electrical currents.
Each material has unique properties that make it suitable for specific applications. For instance, polycarbonate is often used for its transparency and toughness, making it ideal for protective casings and lenses.
Challenges in Injection Mold Manufacturing
Despite its advantages, injection mold manufacturing for electronics poses several challenges. One major challenge is maintaining consistent quality across large production runs. Any variation in the mold can lead to defects in the final product.

Additionally, as electronic devices continue to shrink, molds must be designed with even greater precision. This requires advanced machinery and expertise to ensure that each part meets stringent quality standards.
The Future of Injection Mold Manufacturing
The future of injection mold manufacturing for electronics looks promising. Advances in technology are paving the way for even more precise and efficient manufacturing processes. Innovations like 3D printing and automation are expected to revolutionize the industry, allowing for faster prototyping and production.
As technology evolves, so too will the methods used in injection molding. The focus will continue to be on achieving greater precision and efficiency to meet the ever-growing demands of the electronics industry.